
the ratio of the absolute viscosity ( μ) to the density of the fluid ρ. It can be determined through kinematic viscosity (also called momentum diffusivity), i.e. Find 4 ways to say VISCOSITY, along with antonyms, related words, and example sentences at. For example, a substance with a thick viscosity resists movement while a low viscosity substance moves quickly. In addition to measuring thickness, viscosity measures resistance to motion. An example of a high viscosity liquid is syrup. (2) In fluid dynamics, the term absolute viscosity (or dynamic viscosity) refers to the force per unit area applied tangentially to a fluid, causing the unit rate of displacement of parallel planes separated by a unit distance. Low viscosity refers to substances that are thin, such as water, while high viscosity substances are thick. Therefore, a decreasing ambient temperature will increase the viscosity of a fluid. For instance, the viscosity of a fluid is lower when the temperature is higher. The ambient conditions also affect viscosity. The Birth-Time of the World and Other Scientific Essays by J. External forces such as shear forces or tensile stress act upon the fluid and therefore influence the flow of the fluid. Definition of viscosity in the Fine Dictionary. The molecular structure of a fluid influences viscosity in a way that when the molecules are tightly linked, the higher is the resistance to deformation, and therefore it will have less tendency to flow. (1) The viscosity of a fluid is influenced by the following factors: molecular structure, external forces, and ambient conditions. Temperature Viscosity Relation Viscosity is a measure of a lubricating oil’s resistant to flow. Example: The Viscosity in honey is higher than in water. Oil Viscosity Index and Viscosity Temperature Relation.

It is commonly perceived as 'thickness', or resistance to pouring.

So, the definition of viscosity is-The measurement of the resistance offered by the fluid to deformation at a given is known as the viscosity of the fluid. Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid to deformation under shear stress. Use/Significance in the Earth Science Community: Viscosity is an important measurement in most studies of fluids, from water to oil. Etymology: Speaking of molasses, viscosity comes from the Latin viscosus, which meant sticky. (1) Pitch, which is a dark viscous waxy material derived from tar, could be the most viscous fluid. This is the reason why fluids with excessive viscosity need greater pressure to move than the ones with low viscosity. Viscosity is what it’s referring to, since molasses has a fairly high viscosity and so doesn’t flow very quickly. A fluid’s viscosity is measured by determining its internal resistance to gradual deformation by shear forces or tensile stress.
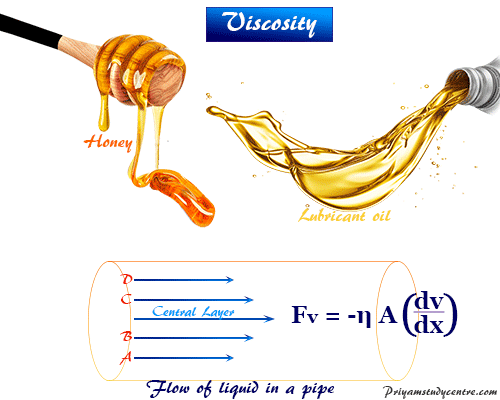
As a physical property, it determines the internal resistance of the fluid to flow. In this experiment we will use Stoke’s Law and the concept of terminal velocity to determine the viscosity of glycerin. It is measured as a physical property of a fluid. Viscosity is a property of uids (liquids and gases) which determines how much resistance is experienced by an object trying to move through the uid. Viscosity refers to the state or condition of being viscous.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
